2025 // Week 34 – Global Pepper Market Analysis: Vietnam & Brazil Situation
Vietnam Pepper Market: Current Price Trends
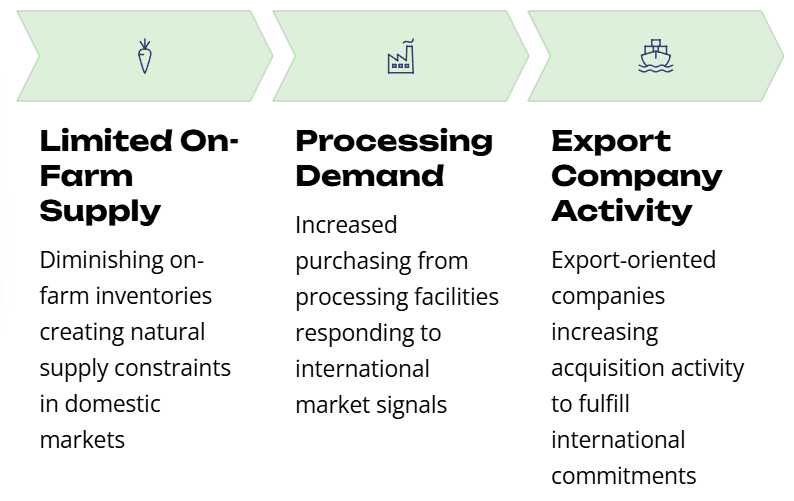
Vietnam’s pepper market is experiencing notable price appreciation, with current values ranging between 143,000-146,000 VND/kg. This upward trajectory represents a significant market development for stakeholders throughout the supply chain. The price movement isn’t merely seasonal fluctuation but appears driven by fundamental market factors that merit careful analysis.
The current price environment reflects a classic supply-demand imbalance, with processing and export companies intensifying their purchasing activities despite limited availability. This suggests these companies may have forward contracts to fulfill or are anticipating continued price appreciation, making current acquisition costs acceptable despite being at multi-month highs.
Global Consumption Recovery & Market Outlook
A notable recovery in global pepper consumption is emerging toward the end of Q3 2025, with particular strength in European and American markets. This consumption uptick coincides with the approach of the year-end holiday season, traditionally a period of peak spice demand across Western markets. The seasonal pattern is especially pronounced in retail and food service segments, which typically increase inventory levels in anticipation of elevated consumer demand.
If current consumption trends maintain their momentum, Vietnamese domestic pepper prices could sustain their upward trajectory in the short term. This positive price environment would create favorable conditions for both farmers with remaining inventory and exporters positioned to fulfill international orders. The timing is particularly advantageous given the current tight supply situation across key producing regions.
The market signals from Europe and the United States are especially significant as these regions represent premium markets with strong purchasing power and established preference for Vietnamese pepper varieties. Their increased activity suggests a potential willingness to accept higher price points, creating a favorable negotiating position for Vietnamese exporters.

Vietnam’s Situation: Production Decline & Supply Constraints
The year 2025 marks a significant milestone in global pepper production trends, representing the fourth consecutive year of worldwide production decline. This multi-year contraction has fundamentally reshaped market dynamics and pricing structures across the industry. In Vietnam specifically, the situation continues to evolve in ways that support price stability and potential appreciation.
Vietnam’s pepper-growing regions continue to experience significant contraction, with total cultivation area expected to reach approximately 110,000 hectares in 2025. This represents a continuation of the acreage reduction trend observed in recent years, as farmers respond to previous periods of price volatility by diversifying into alternative crops. The contraction is particularly pronounced in marginal growing areas where yields and quality have historically been inconsistent.
Despite the reduction in acreage, Vietnam’s production efficiency remains relatively strong, with total output projected at 190,000 tons for 2025. This production level, while substantial in absolute terms, represents a meaningful reduction from peak production years and creates a tighter supply environment that supports price stability. The combination of reduced global production and Vietnam’s specific output constraints provides a strong foundation for prices to maintain their strength through the final months of 2025.
Brazil’s Production: Strategic Expansion
In contrast to Vietnam’s contracting production, according to the Vietnam Pepper and Spice Association (VPSA), Brazil’s pepper industry in 2025 is pursuing a carefully orchestrated expansion strategy. The Brazilian approach reflects a controlled and strategic growth pattern focused on key producing regions with proven success. This expansion comes at a crucial time in the global pepper market and positions Brazil to potentially capture increased market share.
Key Production Regions
Brazil’s pepper production landscape is dominated by several key regions, each with distinct characteristics that influence overall market dynamics:
- Pará: Remains the central production hub with the largest concentration of established farms and processing facilities
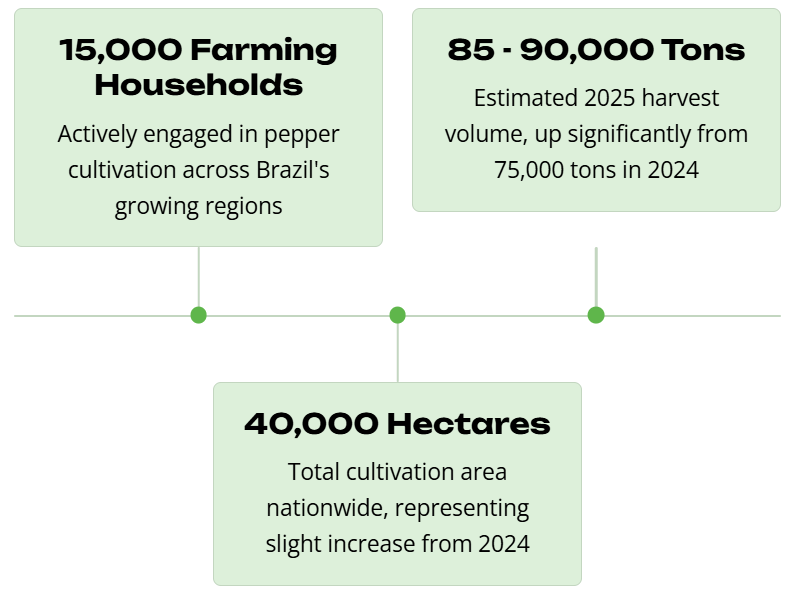
- Sao Mateus: Emerging as an increasingly important secondary region with expanding acreage
- Bahia: Contributing substantially to national output with a combined cultivation area of 17,000-19,000 hectares shared with Sao Mateus

Brazil’s Harvest Cycles & Production Practices
Brazil’s distinctive approach to pepper cultivation creates unique market advantages through its dual-harvest system.
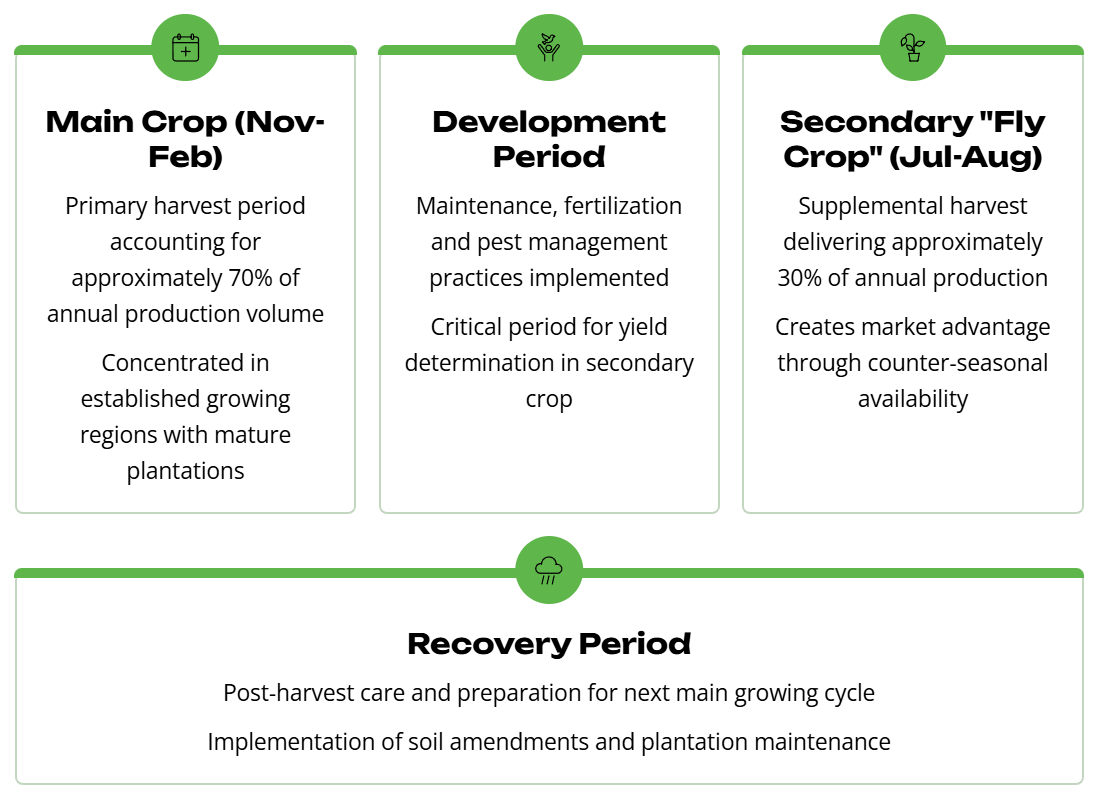
This dual-harvest approach enables Brazilian exporters to maintain a year-round supply capacity, enhancing their reliability as trading partners and creating opportunities to capitalize on seasonal price fluctuations. The staggered production model also helps mitigate risk by distributing potential weather or pest-related challenges across multiple growing periods rather than concentrating vulnerability in a single annual harvest.
The productivity metrics of Brazil’s pepper farms demonstrate strong performance relative to regional averages. With typical yields of 3.2 tons per hectare and large-scale operations achieving up to 3.7 tons per hectare, Brazilian producers maintain competitive efficiency levels that contribute to their expanding market presence. These yield figures reflect sophisticated management practices including optimized planting density at approximately 1,600 poles per hectare and carefully maintained plant heights of 2.5-2.8 meters to facilitate efficient harvesting.
Comparative Analysis & Strategic Implications
The 2025 global pepper market presents a complex but potentially rewarding environment for well-positioned stakeholders. Vietnam’s production decline creates price support that benefits existing producers, while Brazil’s expansion offers growth opportunities without overwhelming the market. The complementary harvest cycles between these major producers may help stabilize year-round availability, potentially reducing the extreme price volatility that has characterized previous market cycles.