Week 53 – Vietnamese Pepper Market Analysis: 2024 Review and 2025 Outlook
Current Pepper Prices and Market Dynamics

As of the final week of 2024, pepper prices in Vietnam have shown a notable rebound, ranging between 150,000 and 151,000 VND/kg. This uptick can be attributed to two primary factors: recent heavy rains in the Central and Central Highlands regions, and an improved purchasing demand driven by year-end festivities. These elements have collectively supported the price increase, providing a positive note for pepper farmers and traders as the year comes to a close.
Despite the price improvement, it’s important to note that market transactions remain at a low volume with slow liquidity. This indicates a cautious approach from buyers and sellers, possibly due to ongoing economic uncertainties or expectations of further price changes. The slow liquidity suggests that while prices have improved, the market is not yet experiencing a surge in trading activity.
In terms of export destinations, the Vietnamese pepper market continues to rely heavily on three key markets: the United States, Germany, and the United Arab Emirates. These countries collectively account for a significant 44.1% of Vietnam’s total pepper export turnover.

*This concentration of export destinations highlights both the strength of Vietnam’s trade relationships with these nations and the potential vulnerability to economic or policy changes in these markets.
2025 Price Forecast and Influencing Factors
As we look ahead to 2025, experts in the pepper industry are predicting a positive trend for prices. The forecast suggests that pepper prices will enter a growth cycle in early 2025, driven by two main factors: a reduction in global supply and rising transportation costs. This combination of supply constraints and increased logistical expenses is expected to put upward pressure on prices, potentially benefiting Vietnamese pepper exporters.
One significant external factor that could influence the pepper market in 2025 is the anticipated rate cuts by the U.S. Federal Reserve (FED). These expected cuts are likely to stimulate economic activity in major importing nations, particularly the United States and countries in the European Union. As these economies receive a boost, it could potentially lead to increased demand for Vietnamese pepper in these key markets. This improved demand could further support the upward trajectory of pepper prices and potentially increase export volumes from Vietnam.

Another crucial factor affecting the 2025 outlook is the delayed harvest due to prolonged drought conditions. The 2025 pepper harvest is expected to be pushed back by approximately two months, which is likely to create a strain on the supply side. This delay has already prompted importers to increase their purchases to cover their needs through the first quarter of 2025. The anticipation of this supply constraint is likely to keep prices elevated and may lead to increased competition among buyers to secure their pepper supplies.
China’s Market Outlook and Global Demand Shifts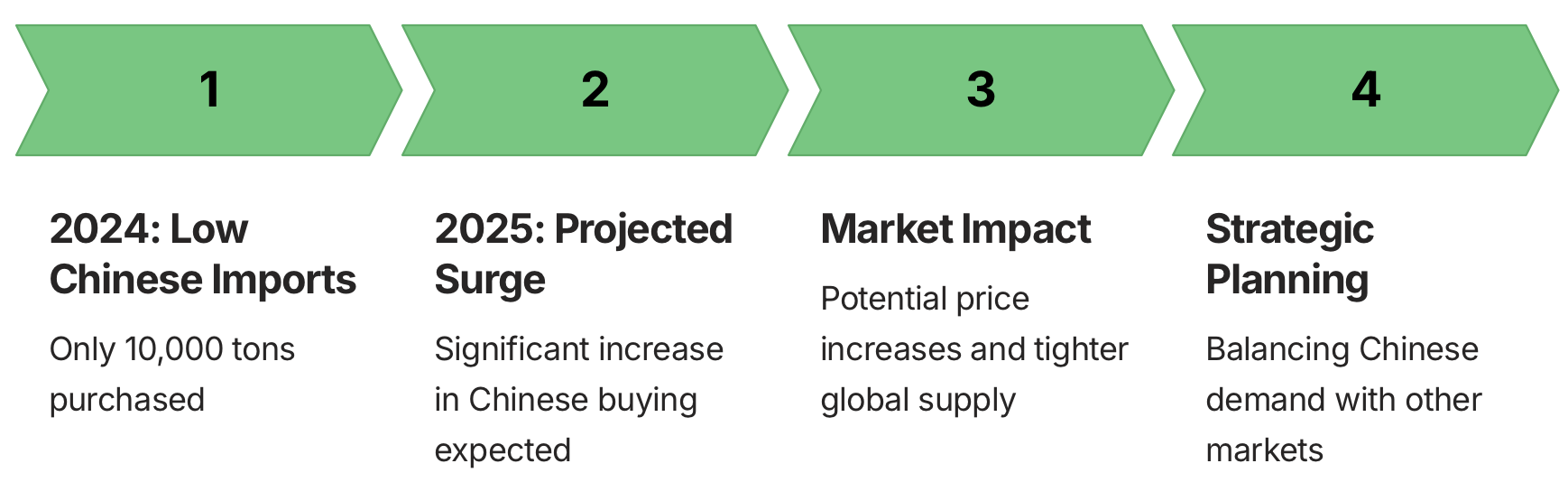
China, a significant player in the global pepper market, is expected to dramatically shift its purchasing patterns in 2025. In 2024, China’s pepper imports from Vietnam were relatively modest, with only 10,000 tons purchased. However, industry analysts anticipate a substantial increase in Chinese buying activity in 2025. This projected surge in demand from China could have far-reaching implications for the global pepper market, potentially driving up prices and tightening supply for other importing nations.
The expected increase in Chinese demand comes at a time when other major markets are in a different position. Many of Vietnam’s regular pepper importers have stocked up sufficiently in 2024, which means they may face less immediate pressure to buy in the early months of 2025. This dynamic creates an interesting market scenario where the increased demand from China could potentially offset any reduction in purchases from other markets.
The shift in Chinese purchasing behavior is likely driven by several factors. These may include changes in domestic consumption patterns, potential shifts in trade policies, or strategic decisions to build up pepper reserves. Whatever the underlying reasons, this anticipated increase in Chinese demand is expected to be a significant factor in shaping the global pepper market in 2025.
For Vietnamese pepper exporters, this projected increase in Chinese demand presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, it could lead to increased sales and potentially higher prices. On the other hand, it may require careful management of supply chains and strategic planning to balance the needs of all markets, ensuring that increased focus on the Chinese market doesn’t come at the expense of long-standing relationships with other key importers.
Vietnam’s Pepper Exports and Revenue in 2024
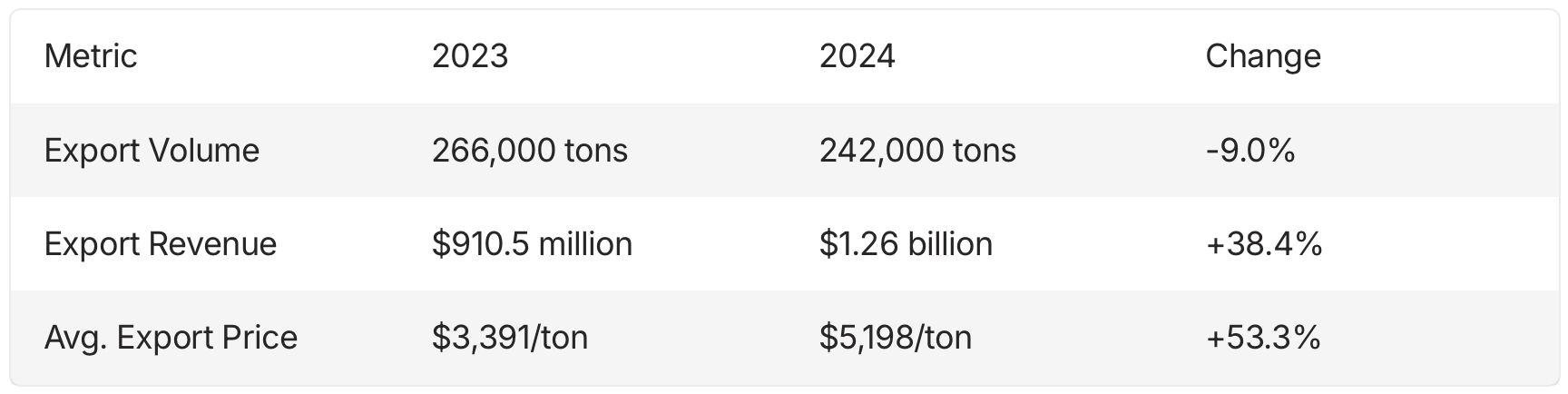
The year 2024 has marked a significant milestone for Vietnam’s pepper industry, with export revenues surpassing $1 billion for the first time since 2017. As of December 15, 2024, Vietnam had exported nearly 242,000 tons of pepper, generating an impressive $1.26 billion in revenue. This figure represents a substantial increase from the $910.5 million earned in 2023, despite a reduction in the total volume shipped by approximately 24,000 tons.
The average export price for Vietnamese pepper in the first 11 months of 2024 stood at $5,198 per ton, marking a significant year-on-year increase of 53.3%. This price increase has been a key driver behind the industry’s strong financial performance, more than offsetting the reduction in export volume. The ability to command higher prices in the international market speaks to the quality and reputation of Vietnamese pepper, as well as favorable market conditions.
The remarkable recovery of Vietnam’s pepper industry in 2024 can be attributed to several factors. These may include improved global demand, strategic marketing efforts, enhanced quality control measures, and possibly favorable exchange rates. The industry’s ability to increase revenue while reducing volume also suggests a shift towards higher-value products or markets, indicating a maturing and increasingly sophisticated approach to international trade.

*This strong performance in 2024 sets a positive foundation for the industry moving into 2025. However, it also raises questions about sustainability and whether such high prices and revenues can be maintained in the face of increasing global competition and potential market volatility.
Global Supply and Demand Projections
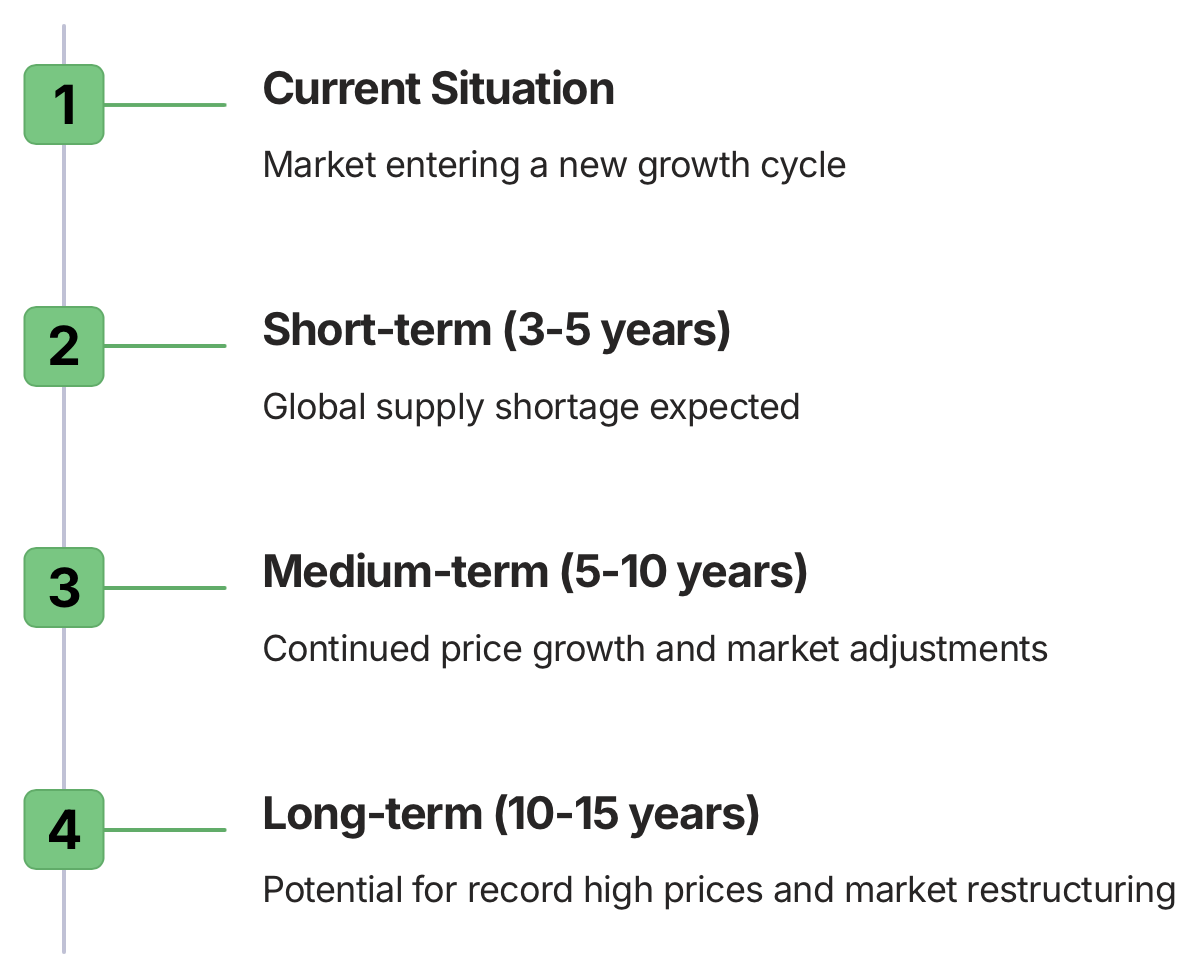
Agricultural experts are projecting a significant imbalance in the global pepper market over the coming years. Their forecasts indicate a 3-5 year period where global supply will be unable to meet consumption demands. This supply shortage is expected to have far-reaching implications for the pepper industry, potentially driving prices to new heights and reshaping market dynamics.
The projected supply shortage is part of a larger cycle in the pepper market. Experts believe that a new 10-15 year price growth cycle has begun, which could see pepper prices reaching record highs. This long-term trend suggests that the current high prices are not just a short-term anomaly, but part of a sustained market shift that could benefit major producing countries like Vietnam for years to come.
Several factors are contributing to this projected supply-demand imbalance. On the supply side, issues such as climate change, shifting agricultural practices, and potential diseases affecting pepper plants could limit production growth. Meanwhile, on the demand side, increasing global population, changing culinary trends, and the growing popularity of pepper in various industries beyond food (such as medicinal and cosmetic applications) could be driving consumption higher.
For Vietnam, as one of the world’s largest pepper producers, this projected global shortage presents both opportunities and challenges. While higher prices could boost revenues, there will likely be increased pressure to boost production to meet global demand. This could lead to intensified cultivation practices, potentially raising concerns about sustainability and environmental impact. Additionally, the high prices might incentivize other countries to increase their pepper production, potentially leading to increased competition in the long term.
International Pepper Price Comparisons
To provide context for Vietnam’s pepper prices and competitiveness in the global market, it’s crucial to examine the latest international pepper prices. According to the most recent data from the International Pepper Community (IPC), there are significant variations in pepper prices across different producing countries and pepper types.
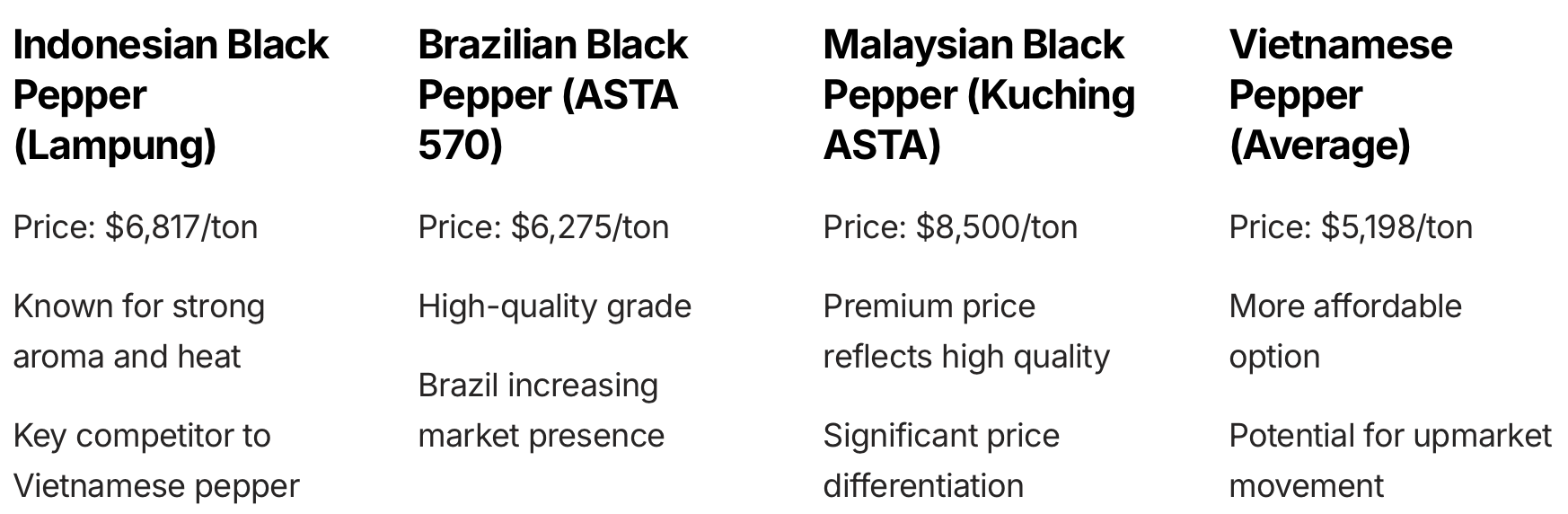
Indonesian Black Pepper (Lampung) is currently priced at $6,817 per ton. This variety, known for its strong aroma and heat, is a key competitor to Vietnamese pepper in the global market. The relatively high price of Indonesian pepper may provide an opportunity for Vietnamese exporters to offer competitive pricing while still maintaining healthy profit margins.
Brazilian Black Pepper (ASTA 570) is priced at $6,275 per ton. Brazil has been increasing its presence in the global pepper market in recent years, and this price point puts it in a competitive position. The ASTA 570 grade indicates a high-quality product, suggesting that Brazil is targeting the premium segment of the market.
Malaysian Black Pepper (Kuching ASTA) commands the highest price among the three, at $8,500 per ton. This premium price reflects the reputation of Malaysian pepper for its quality and consistency. The significant price difference between Malaysian and other peppers highlights the potential for price differentiation based on origin and perceived quality in the global pepper market.
Comparing these prices to the average export price of Vietnamese pepper ($5,198 per ton in 2024), it’s clear that Vietnamese pepper is positioned as a more affordable option in the global market. This pricing strategy may help explain Vietnam’s success in capturing a large market share and achieving record export revenues. However, it also raises questions about whether there’s potential for Vietnam to move upmarket and capture some of the premium price points seen with Malaysian or Indonesian peppers.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
The Vietnamese pepper industry has demonstrated remarkable resilience and growth in 2024, achieving a significant milestone by surpassing $1 billion in export revenue for the first time since 2017. This achievement, coupled with a 53.3% year-on-year increase in average export prices, positions Vietnam strongly in the global pepper market. The industry’s ability to increase revenue despite a decrease in export volume highlights improved value capture and market positioning.
Looking ahead to 2025, several factors are expected to influence the market dynamics:
- Anticipated price growth cycle driven by global supply shortages and rising transportation costs
- Delayed harvest in Vietnam due to prolonged drought, potentially straining supply
- Expected increase in demand from China, offsetting potentially reduced immediate buying pressure from other markets
- Potential stimulation of demand in key markets like the U.S. and EU due to expected Federal Reserve rate cuts
The long-term outlook for the pepper industry appears positive, with agricultural experts projecting a 3-5 year global supply shortage and the beginning of a new 10-15 year price growth cycle. This could lead to sustained high prices and potential record highs in the coming years.
However, challenges remain. Vietnam’s pepper industry must navigate the balance between meeting increased demand and maintaining sustainable practices. There’s also the potential for increased competition as high prices may incentivize other countries to boost their pepper production.
In conclusion, while the Vietnamese pepper industry is currently in a strong position, continued success will depend on strategic management of production, quality control, and market relationships. The industry should also consider exploring opportunities to move into premium market segments, potentially capturing higher price points similar to those seen with Malaysian or Indonesian peppers. By leveraging its current strengths and adapting to changing market conditions, Vietnam’s pepper industry is well-positioned to maintain its leading role in the global pepper trade.

