2025 // Week 20 – Vietnam Pepper Market Update and Outlook: Q2 2025
Current Domestic Price Trends
Vietnam’s domestic pepper market has experienced a notable downward trend in recent weeks, with prices currently stabilizing at 154,000 – 155,000 VND/kg. The weekly summary indicates an average decline of 2,000 – 3,000 VND/kg across pepper-growing regions, with the most significant drop occurring in the Central Highlands provinces of Đắk Lắk and Đắk Nông, where prices fell by 3,000 VND/kg. This regional variance has created an unusual market dynamic where prices in the Southeast region are currently higher than those in the traditionally dominant Central Highlands growing areas.
Pepper price developments in the Central Highlands and Southeast from First 2023 to May 12, 2025 (Unit: VND/kg)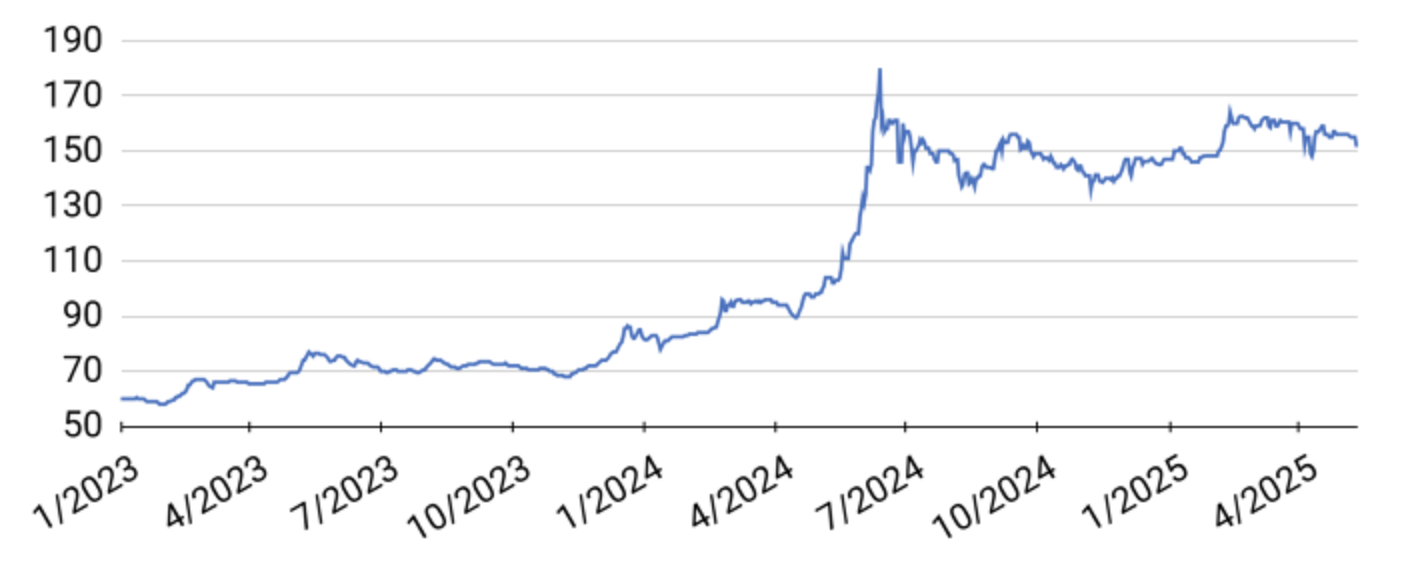
The price decline appears to be part of a broader market correction following earlier gains in the season. Market analysts attribute this downward pressure to a combination of factors including seasonal selling patterns, global market uncertainties, and cautious buyer behavior ahead of potential regulatory changes. The current price level represents a critical threshold in the market, with industry experts closely monitoring whether prices will stabilize at this point or continue downward.
Global Market Movements and Trade Dynamics
The global pepper market is currently experiencing mixed trends that significantly impact Vietnam’s position as a leading exporter. While prices have increased in Indonesia, creating competitive pressure, India has seen price decreases that may provide opportunities for market share adjustments. Industry experts emphasize that the current market is being driven more by trade dynamics between countries than by traditional supply-demand fundamentals, creating a complex and sometimes unpredictable market environment.
Vietnam’s Pepper Export-Import Performance
Vietnam’s pepper export-import data for April 2025 and year-to-date figures reveal significant shifts in the country’s trade patterns. Despite a decline in export volumes due to limited domestic supply, export values continue to rise, indicating strong pricing power in international markets. This value-volume divergence suggests Vietnam’s success in positioning its pepper as a premium product commanding higher prices despite reduced quantities.
Concurrently, Vietnam has significantly increased its pepper imports during January-April 2025, with total imports reaching 15,374 tons, representing a 25.3% year-over-year increase in volume and a remarkable 104.8% increase in value. This substantial growth in imports reflects Vietnam’s evolving role as both a producer and a processing hub in the global pepper trade. The country imports raw pepper from various sources, adds value through processing and quality control, and then re-exports to premium markets worldwide.
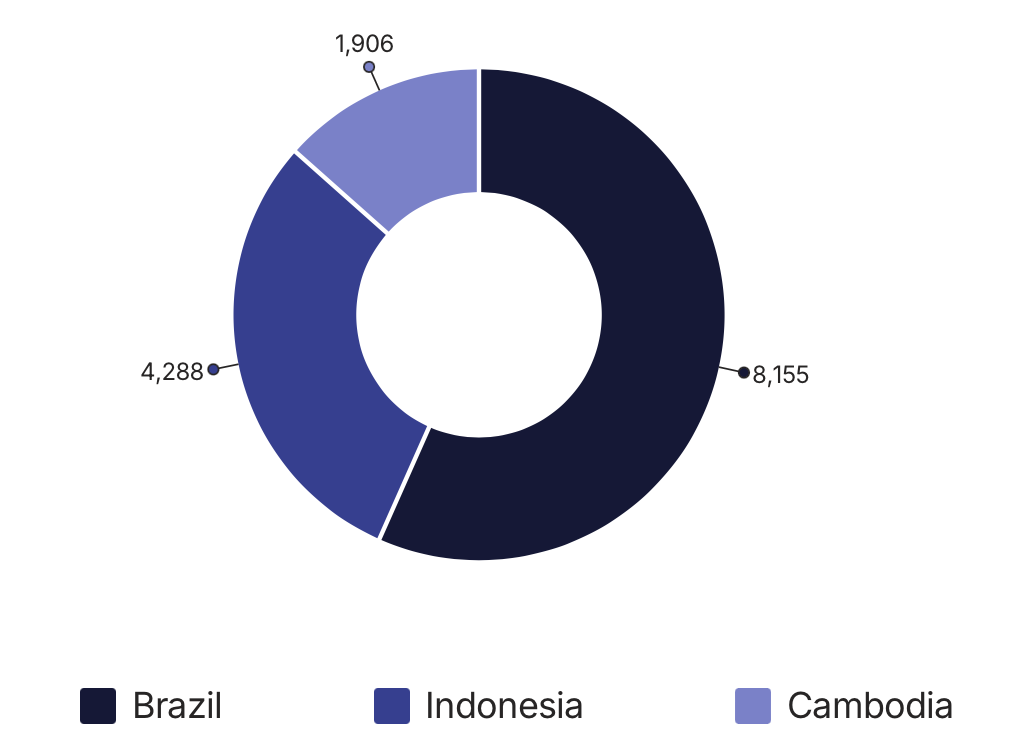
The top import sources showcase interesting dynamics in regional pepper trade. Brazil leads as Vietnam’s primary import source with 8,155 tons, a 33.1% increase from the previous year. Indonesia has dramatically increased its exports to Vietnam with 4,288 tons, representing a massive 207.8% year-over-year growth. In contrast, imports from Cambodia have declined significantly, falling by 49.3% to 1,906 tons. These shifting import patterns reflect changing regional production capabilities, pricing competitiveness, and strategic sourcing decisions by Vietnamese processors looking to maintain quality and volume requirements for their export markets.
Export Destinations and Market Diversification
Vietnam’s pepper export destinations reveal both established patterns and emerging opportunities for market diversification. The United States remains Vietnam’s top pepper buyer, maintaining its position as the premier destination despite the looming tariff concerns. This continued strong relationship underscores the quality reputation that Vietnamese pepper has established in the demanding U.S. market and highlights the importance of maintaining this key trading partnership despite regulatory challenges.
Perhaps the most notable development in Vietnam’s export landscape is the dramatic rise in shipments to China, which increased by an impressive 160% in April alone. Despite this remarkable growth, China currently ranks only sixth among Vietnam’s top pepper buyers, indicating significant potential for further expansion in this massive neighboring market. The surge in Chinese demand could represent a valuable opportunity for market diversification as Vietnam navigates challenges in other traditional markets.

Vietnam’s white pepper exports show a distinct pattern, with China, Germany, and the United States emerging as the top buyers for this premium product. This specialized market segment allows Vietnam to command higher prices and cater to specific culinary and industrial applications. The diversification across both black and white pepper varieties enables Vietnamese exporters to target different market segments and reduce dependency on any single product category or destination market.
Short-Term Market Outlook and Risk Assessment
The immediate market outlook for Vietnamese pepper remains bearish in the short term, with technical indicators suggesting continued downward pressure on prices. The market experienced two distinct price declines last week—one at the beginning and another at the end of the week—reinforcing the current negative sentiment. Market participants are maintaining a cautious approach, closely monitoring two critical factors that could influence near-term price movements: fluctuations in the USD exchange rate and ongoing trade negotiations that could affect export competitiveness.
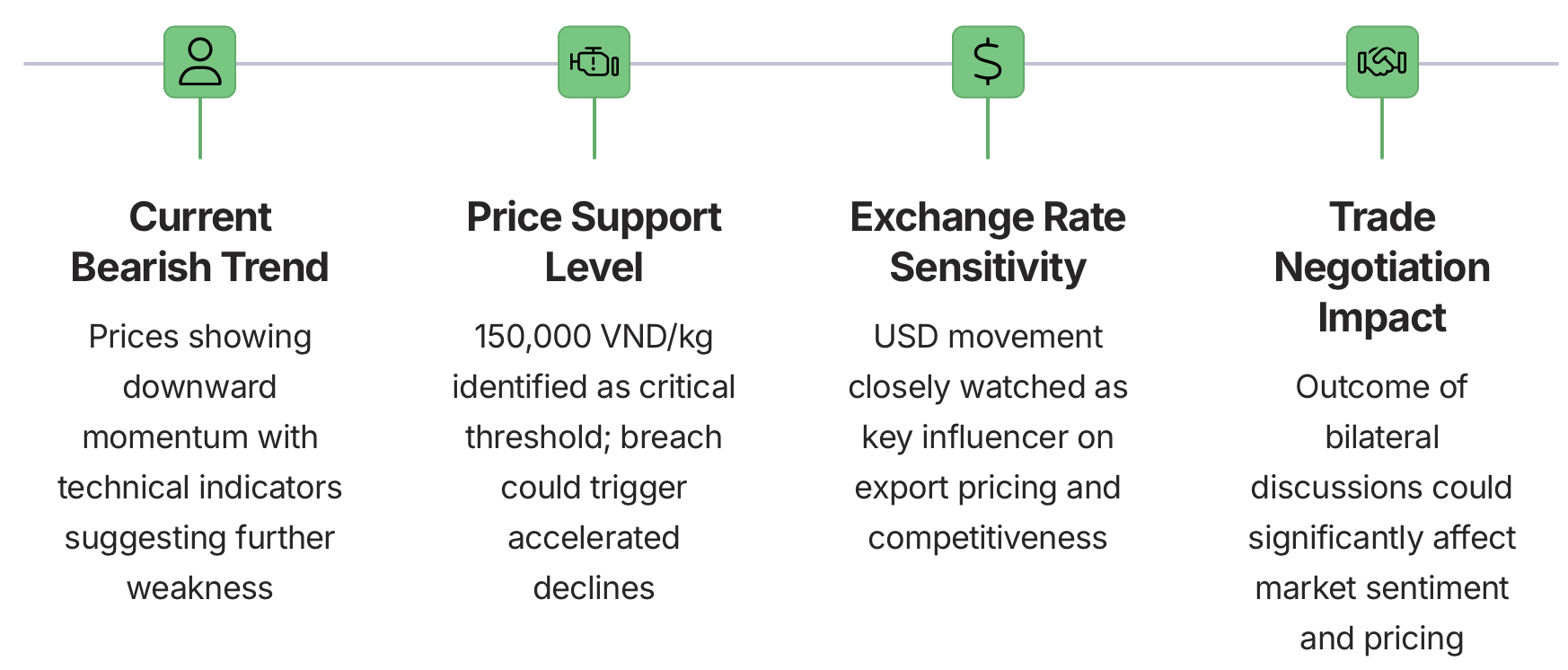
Market analysts have identified 150,000 VND/kg as a critical psychological and technical support level. If prices break below this threshold, technical analysis suggests the possibility of an accelerated decline as more producers and holders may decide to liquidate inventories rather than risk further price deterioration. This potential cascade effect could intensify selling pressure and drive prices lower in the immediate term.
The cautious market sentiment is further reinforced by uncertainties surrounding USD movements and international trade negotiations. As a globally traded commodity priced predominantly in USD, pepper prices are inherently sensitive to currency fluctuations. Additionally, the outcome of ongoing trade discussions, particularly with the United States regarding tariff levels, could significantly impact Vietnam’s export competitiveness and, consequently, domestic price levels. These interrelated factors create a complex risk environment that market participants must navigate carefully in the coming weeks.
Medium-Term Outlook for Q2 2025
Despite the current bearish conditions, market analysts see potential for a rebound in Vietnam’s pepper market later in May 2025. This optimism is bolstered by several positive factors, including encouraging U.S. economic indicators that suggest robust demand in this key export market. The fundamental supply-demand dynamics also appear supportive of a recovery, with limited domestic supply facing rising global demand—a combination that typically leads to price appreciation in agricultural commodities.
The overall Q2 2025 outlook hinges on several critical factors that could either accelerate or impede the anticipated recovery. Demand from the Middle East and European Union will play a pivotal role, as these regions represent significant volumes and value in Vietnam’s export portfolio. Any shifts in purchasing patterns or regulatory requirements from these markets could substantially impact Vietnam’s export performance and, consequently, domestic price levels.
Another crucial determinant of Vietnam’s Q2 performance will be the competitive landscape, particularly regarding export competition from Brazil and Indonesia. These major producing countries face lower U.S. tariff rates compared to Vietnam, potentially giving them a competitive advantage in the American market. If these competitors aggressively target U.S. buyers with lower prices, Vietnam may face pressure to reduce prices to maintain market share, or alternatively, to redirect exports to other markets, potentially creating oversupply situations in those destinations. The complex interplay between these competing producers will significantly influence global pepper trade flows and price formation throughout the quarter.
Strategic Challenges and Recommendations for Vietnamese Exporters
Vietnam’s pepper industry faces significant challenges in the evolving global market landscape, with U.S. tariffs presenting perhaps the most immediate obstacle. These higher tariff rates compared to those imposed during the Trump administration place Vietnamese exporters at a competitive disadvantage relative to producers from countries facing lower duty rates. This situation demands a strategic response to maintain market position and profitability in an increasingly competitive environment.
Market Diversification
Vietnamese exporters must intensify efforts to expand beyond traditional markets, particularly focusing on Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. These regions offer significant growth potential and can help reduce overdependence on the U.S. market where tariff challenges are most acute.
- Target high-growth markets like China where recent export growth has been exceptional
- Strengthen presence in Middle Eastern hubs like UAE that show strong buying interest
- Develop strategies for premium European markets valuing sustainability and quality
Quality Enhancement
To command premium prices and offset tariff disadvantages, Vietnam must continue elevating product quality and consistency. Investments in processing technology, certification, and quality control systems will be essential competitive tools.
- Implement advanced sorting and cleaning technologies to ensure consistent quality
- Expand organic and sustainable certification programs to access premium market segments
- Develop traceability systems that provide transparency from farm to consumer
Value-Added Processing
Moving up the value chain through increased processing can help Vietnam capture greater value from pepper exports while differentiating from commodity-focused competitors. Developing specialized products for specific market segments represents a key opportunity.
- Expand production of premium white pepper for specialized markets
- Develop consumer-ready packaging and branded products rather than bulk exports
- Explore pepper derivatives and specialized extracts for food industry applications

