2025 // Week 18 – Vietnam Pepper Market Report: Growing Exports and Global Price Trends
Current Domestic Market Conditions
Vietnam’s domestic pepper market has shown remarkable stability in recent weeks, with prices maintaining consistent levels despite various market pressures. As of the most recent trading period, black pepper prices remained unchanged compared to the end of the previous week, hovering in the range of 156,000 to 157,000 VND/kg (approximately 6.30-6.35 USD/kg). This stability represents a positive indicator for local producers who have weathered significant price volatility in recent years.
Pepper price developments in the Central Highlands and Southeast from First 2023 to April 26, 2025 (Unit: VND/kg)

The market is currently experiencing increased buying activity across multiple trading hubs throughout Vietnam’s key pepper-growing regions. This heightened demand is providing crucial support for domestic pepper prices, preventing potential downward pressure that might otherwise occur during periods of increased harvest volume. Local traders report that both domestic buyers and export-oriented companies have been actively purchasing available stocks, contributing to the overall market strength.
Export Performance Analysis: Q1 2025
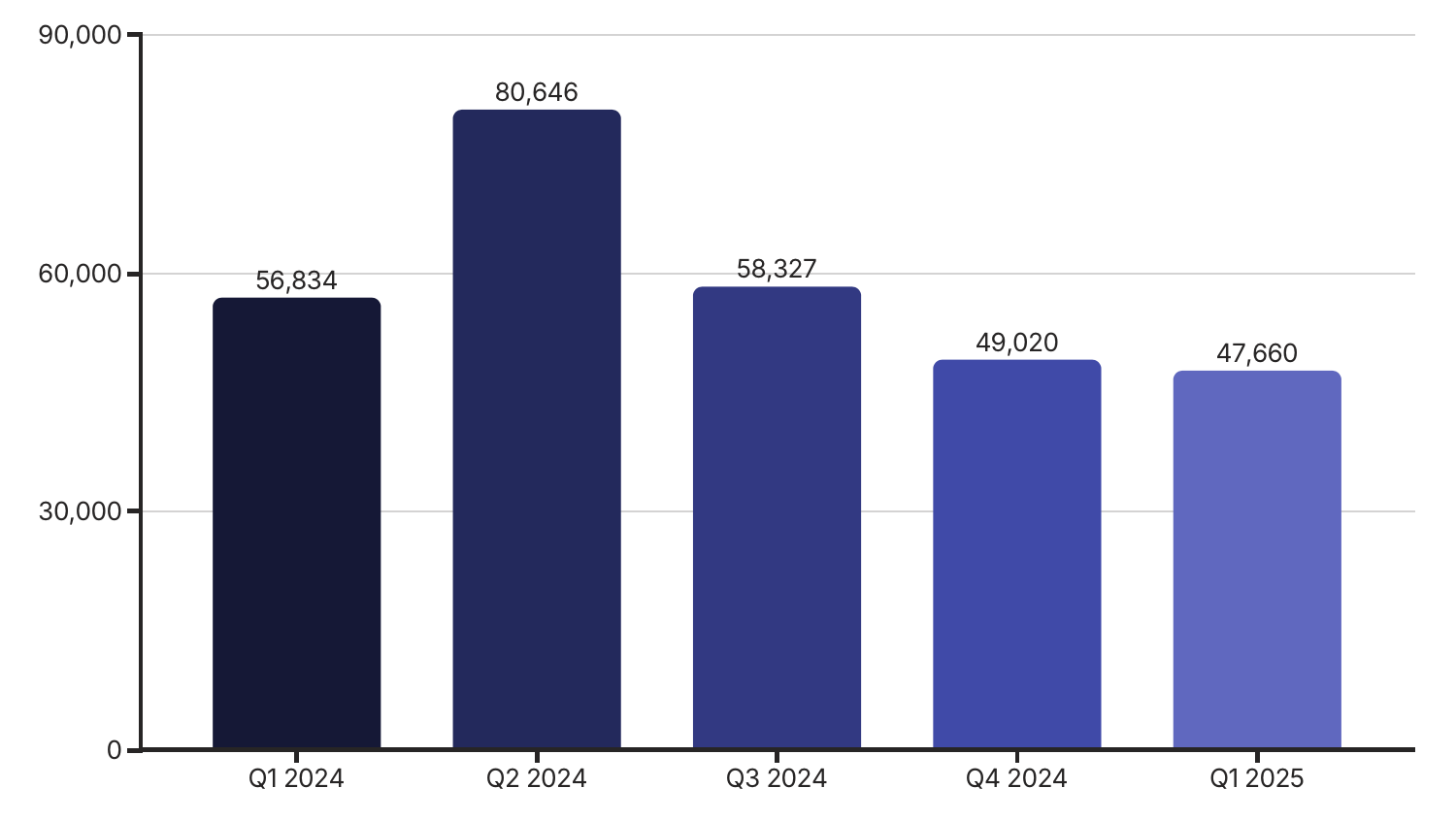 Vietnam’s pepper export sector has demonstrated impressive growth in the first quarter of 2025, establishing a strong foundation for the year’s overall performance. By the end of Q1, Vietnam had successfully exported 47,660 tons of pepper, encompassing both black and white varieties. Total export turnover almost hit 330 million USD, up 38.6% year-on-year, despite a moderate decrease in export volume compared to Q1 2024. The increase in value was driven by higher average export prices, particularly from premium product lines, and a shift in volume away from lower-priced bulk shipments.
Vietnam’s pepper export sector has demonstrated impressive growth in the first quarter of 2025, establishing a strong foundation for the year’s overall performance. By the end of Q1, Vietnam had successfully exported 47,660 tons of pepper, encompassing both black and white varieties. Total export turnover almost hit 330 million USD, up 38.6% year-on-year, despite a moderate decrease in export volume compared to Q1 2024. The increase in value was driven by higher average export prices, particularly from premium product lines, and a shift in volume away from lower-priced bulk shipments.
This growth trend underscores Vietnam’s continued dominance in the global pepper trade despite increasing competition from other producing countries.
The export performance can be attributed to several factors, including improved product quality, strategic market diversification efforts, and favorable price dynamics in key destination markets. Vietnamese exporters have successfully leveraged their reputation for reliability and consistent quality to secure new contracts and expand existing relationships with international buyers. Additionally, investments in post-harvest processing technologies have enabled exporters to meet increasingly stringent quality requirements in premium markets, allowing them to command higher prices for their products.
China Market Dynamics: Opportunities and Challenges
China has emerged as a market of significant interest for Vietnamese pepper exporters, with recent data revealing noteworthy shifts in import patterns. In Q1 2025, China imported 2,034 tons of Vietnamese pepper, representing a dramatic 88% increase compared to the same period last year. This substantial growth is primarily attributed to depleted domestic reserves, forcing Chinese buyers to increase international procurement to meet domestic demand requirements.
However, despite this impressive year-over-year growth, current import volumes remain significantly below historical norms. In previous years, China typically imported between 50,000 and 60,000 tons of pepper annually from Vietnam, making the current figure of just over 2,000 tons for a quarter still relatively modest. This discrepancy suggests substantial untapped potential for growth as Chinese inventories continue to decrease and domestic consumption patterns normalize following disruptions in recent years.
U.S. Market: Navigating Trade Policy Changes
The United States market presents both significant opportunities and challenges for Vietnamese pepper exporters in 2025. A recent development of critical importance is the temporary suspension of higher retaliatory tariffs by the U.S., which has instead implemented a more moderate 10% tariff for a 90-day period. This policy shift creates what industry experts characterize as a “temporary pause” in escalating trade tensions between the two nations, opening a strategic window for Vietnamese exporters.
The second quarter of 2025 represents what many industry observers are calling a “golden window” for Vietnamese pepper exporters to strengthen their position in the American market. This limited-time opportunity demands urgent action from exporters to secure and potentially expand their market share in one of the world’s most valuable pepper importing markets. Companies are actively engaging with U.S. distributors, participating in trade shows, and exploring direct-to-consumer channels to capitalize on this temporary tariff reduction.

Industry analysts emphasize that while the temporary tariff reduction provides immediate relief, the long-term sustainability of Vietnam’s position in the U.S. market will depend on developing strategies that can remain viable even if higher tariffs are reinstated. This includes focusing on premium market segments where quality rather than price is the primary purchasing factor, and developing direct relationships with end users to create brand loyalty that can withstand price fluctuations.
Strategic Initiatives in the Vietnamese Pepper Industry
Vietnamese pepper businesses are actively implementing multifaceted strategies to ensure long-term competitiveness in an increasingly challenging global marketplace. These strategic initiatives focus on geographic diversification, technological advancement, and quality enhancement, representing a comprehensive approach to securing the industry’s future prosperity.
Market Expansion Efforts
Companies are systematically pursuing geographic diversification strategies, reducing reliance on any single export destination. This approach includes developing specialized marketing approaches for different regions, understanding local consumer preferences, and establishing direct relationships with regional distributors. Emerging markets in Eastern Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa are receiving particular attention as high-potential growth areas with fewer regulatory barriers than traditional Western markets.
Partner Diversification
Beyond geographic expansion, Vietnamese exporters are diversifying their business relationships, moving from single-buyer dependencies to multiple-partner networks. This strategy involves cultivating relationships with various types of buyers including international trading companies, food manufacturers, retail chains, and specialty distributors. By maintaining a diverse portfolio of partners, companies can better withstand disruptions in any single business relationship and gain valuable market intelligence from multiple perspectives.
Technological Investment
Significant capital is being directed toward technological modernization throughout the supply chain. Advanced sorting machines, steam sterilization equipment, and precision packaging systems represent just a few areas of focus. These investments enhance Vietnam’s ability to meet increasingly stringent global quality standards while improving production efficiency. Additionally, implementation of traceability systems using blockchain technology is providing transparency that premium buyers increasingly demand.
Global Production Trends and Market Supply
Global pepper production continues to exhibit a concerning downward trajectory, with significant implications for market dynamics and pricing trends. According to the latest comprehensive market analysis, world pepper production in 2025 is forecasted to decrease by a substantial 6.1% compared to the previous year. This decline is not uniformly distributed, with particularly significant reductions expected in India, Indonesia, and Sri Lanka.
Multiple factors are contributing to this production decline across various growing regions. In India, unusual weather patterns including extended dry periods followed by excessive rainfall have damaged flowering and fruit development in key growing regions. Indonesian production continues to be affected by aging plantations and insufficient replanting initiatives, compounded by labor shortages in rural areas. Sri Lanka’s pepper industry faces challenges from disease pressures and economic constraints limiting investment in plantation maintenance and renewal.
Market experts unanimously predict that this continuing production decline will exert upward pressure on global pepper prices in the coming months. Specifically for the Vietnamese market, analysts anticipate a notable price increase following the country’s holiday period. This prediction is based on the combination of reduced global supply, steadily increasing demand in key markets, and the expectation that processors will need to replenish inventories that were depleted during the first quarter.
Current International Pepper Prices and Competitive Positioning
The International Pepper Community (IPC), the authoritative global body for pepper market information, provides crucial insights into current pricing dynamics across major producing countries. As of the latest trading session, IPC data reveals a complex but generally strengthening price environment across various origins and grades, with notable variations that highlight the importance of quality differentiation and origin-specific market dynamics.


*Source: VPSA – Vietnam Pepper and Spice Association
Vietnamese pepper prices demonstrate the country’s competitive positioning in the international market. Currently, Vietnamese black pepper with 500 g/l grade is trading at 6,800 USD/ton, while the premium 550 g/l grade commands a higher price of 6,900 USD/ton. Vietnamese white pepper, known for its exceptional quality and cleanliness, is currently valued at 9,800 USD/ton, positioning it competitively against Indonesian Muntok white pepper and at a price advantage compared to Malaysian white pepper.
The IPC’s resumption of upward price adjustments for Indonesian pepper varieties signals broader market strengthening, likely reflecting recognition of the tightening global supply situation. This development is particularly significant for Vietnamese exporters, as Indonesian prices often influence regional price trends and buyer expectations. The modest but consistent price increases observed across multiple origins suggest a market that is gradually transitioning from a period of stability to one of controlled appreciation, creating favorable conditions for Vietnamese exporters to implement modest price increases without sacrificing market share.

